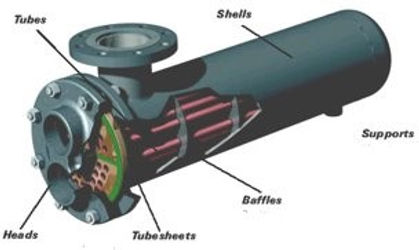
1. SHELL & TUBE
Shell with tubes inside it
1 fluid runs through the tubes
The other fluid runs over the tubes
Heat is tranferred in this way
Set of tubes is a tube bundle
Different types of tubes: plain...
Features
Applicable to a wide range of
pressure and temperature conditions
Widely known most common type of heat exchanger
Big, Expensive maintenance
Subject to flow induced vibrations – may lead to equipment failure
Contains dead/stagnant zones on the sides of the shell which could lead to corrosion issues
2. GASKETED PLATE

Thin corrugated plates fitted with gaskets
Plates compressed into rigid frame
Parallel flow channels with max
turbulance
Fluids enters at top & bottom of exchanger
Fluid flows in alternative channels
Follows counter current principle
Features
High thermal efficiency
Compact design so small quantities of materials are used for heat transfer surface
High performance
Low installation cost
Gasketed design, plates can be easily dismantled, allowing easy and rapid cleaning
Versatile design can easily adjust capacity of heat exchanger by adding or removing plates
Environmentally efficient
Gasketed plates are sealed tight, however these heat exchangers are more prone to leakage than shell and tube
Not efficient for fluids with huge temperature differences, these tend to be used for fluids with minimal/ normal temperature differences
3. SPIRAL

Circular
Two concentric spiral
channels
Each channel is for one fluid
Curved channels
Allows max heat transfer
Small overall unit size
Features
Self cleaning effect, reduces operating costs
Low maintenance cost due to easy access
High heat transfer efficiency, better than shell and tube
Can handle two highly fouling fluids
Each unit is fully drainable
Condensers have virtually no vapour side pressure drop
Column mounting of condensers reduces installation costs
Usually have limitations on the maximum temperature and pressure allowed to reach
Tend to have a lower volumetric flowrate than other types of heat exchangers



